Comprehensive Guide to Hand and Wrist Anatomy and Conditions
The human hand enables us to perform many of our daily activities such as driving, writing, and cooking. Yet all too often we take the ability to grip and grasp for granted, because we have been doing it all of our lives. Yet for anyone who has suffered from conditions or injuries to their hands and wrists, it can be extremely debilitating, uncomfortable, and painful. You deserve to use your hands and wrists without pain – we’re here to help.
To help you discuss hand and wrist conditions and treatment options with your surgeon, here’s a breakdown of the anatomy of the hand and wrist.
Guía Completa de Anatomía y Condiciones de la Mano y Muñeca
La mano humana nos permite realizar muchas de nuestras actividades diarias, como conducir, escribir y cocinar. Sin embargo, a menudo damos por sentada la habilidad de agarrar y sostener, porque lo hemos hecho toda la vida. Para quienes han sufrido condiciones o lesiones en manos y muñecas, puede ser extremadamente debilitante, incómodo y doloroso. Usted merece usar sus manos y muñecas sin dolor; estamos aquí para ayudar.
Para ayudarle a discutir condiciones y opciones de tratamiento de la mano y muñeca con su cirujano, aquí hay un desglose de la anatomía de la mano y muñeca.
- AnatomyAnatomía
- Conditions Condiciones
- Procedures Cirugías
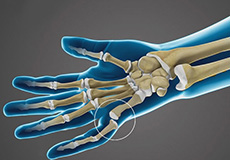
Hand & Wrist Anatomy
The hand is made up of the wrist, palm, and fingers, and consists of 27 bones, 27 joints, 34 muscles, more than 100 ligaments and tendons, and many blood vessels and nerves.
Bones of the Hand
The wrist is composed of eight carpal bones, which attach to the radius and ulna to form the wrist joint, and the five metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each metacarpal bone connects to one finger at a metacarpophalangeal joint, also known as the knuckle. The joint closest to the knuckle is the proximal interphalangeal joint, and the joint closest to the end of the finger is the distal interphalangeal joint. Both act like hinges when the fingers bend and straighten.
The bones in our fingers and thumb are called phalanges. Each finger has three phalanges separated by two interphalangeal joints and the thumb has only two phalanges and one interphalangeal joint.
Articular cartilages are smooth material that act as shock absorbers and cushion the ends of bones at each of the 27 joints, allowing smooth movement of the hand.
Ligaments function to control the movement of the hand.
Muscles of the Hand
There are two types of muscles in the hand.
- Intrinsic muscles are small muscles that originate in the wrist and hand, and are responsible for fine motor movements of the fingers.
- Extrinsic muscles originate in the forearm or elbow, control the movement of the wrist and hand, and are responsible for gross hand movements. Each finger has three extrinsic and three intrinsic muscles. The index and little finger each have an extra extrinsic extensor.
Ligaments of the Hand
Each finger joint has two collateral ligaments on either side, which stop the joints from bending sideways. The volar plate is the strongest ligament in the hand, and joins the proximal and middle phalanx on the palm side to prevent backward bending, hyperextension.
Tendons of the Hand
The extrinsic muscles are attached to finger bones through long tendons that extend from the forearm through the wrist. Flexor tendons on the palm side help in bending the fingers, while extensor tendons on top of the hand help straighten the fingers.
Nerves of the Hand
The three main nerves of the hand and wrist originate at the shoulder and travel down the arm to the hand:
- The ulnar nerve crosses the wrist through an area called Guyon’s canal and branches to provide sensation to the little finger and half of the ring finger.
- The median nerve crosses the wrist through a tunnel called the carpal tunnel, providing sensation to the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger and part of the ring finger.
- The radial nerve runs down the thumb side of the forearm and provides sensation to the back of the hand from the thumb to the middle finger.
Blood Vessels of the Hand
The main arteries are the ulnar and radial arteries, which supply blood to the front of the hand, fingers, and thumb. The ulnar artery travels next to the ulnar nerve through the Guyon’s canal in the wrist. The radial artery is the largest artery of the hand, traveling across the front of the wrist, near the thumb. Other blood vessels travel across the back of the wrist to supply blood to the back of the hand, fingers and thumb.
If you’re suffering from injuries, problems, or pain to your hand and wrist, let us help you get a grip on your condition — and get your back your comfort and quality of life.
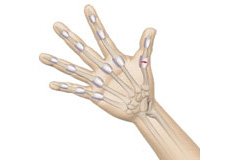
Anatomía de la Mano y Muñeca
La mano está compuesta por la muñeca, palma y dedos, y consta de 27 huesos, 27 articulaciones, 34 músculos, más de 100 ligamentos y tendones, y muchos vasos sanguíneos y nervios.
Huesos de la Mano
La muñeca está compuesta por ocho huesos carpianos, que se unen al radio y ulna para formar la articulación de la muñeca, y los cinco huesos metacarpianos que forman la palma. Cada metacarpiano se conecta a un dedo en la articulación metacarpofalángica, también conocida como nudillo. La articulación más cercana al nudillo es la interfalángica proximal, y la más cercana a la punta del dedo es la interfalángica distal. Ambas actúan como bisagras al doblar y estirar los dedos.
Los huesos de los dedos y pulgar se llaman falanges. Cada dedo tiene tres falanges separadas por dos articulaciones interfalángicas, y el pulgar tiene dos falanges y una articulación interfalángica.
Los cartílagos articulares son materiales lisos que actúan como amortiguadores y protegen los extremos de los huesos en cada una de las 27 articulaciones, permitiendo movimiento suave.
Los ligamentos controlan el movimiento de la mano.
Músculos de la Mano
Hay dos tipos de músculos en la mano:
- Músculos intrínsecos: pequeños, originados en la muñeca y mano, responsables de movimientos finos de los dedos
- Músculos extrínsecos: originados en el antebrazo o codo, controlan movimiento de la muñeca y mano, responsables de movimientos gruesos de la mano. Cada dedo tiene tres músculos extrínsecos y tres intrínsecos. El índice y meñique tienen un extensor extrínseco adicional.
Ligamentos de la Mano
Cada articulación de los dedos tiene dos ligamentos colaterales a cada lado que evitan que las articulaciones se doblen lateralmente. La placa volar es el ligamento más fuerte de la mano, y une la falange proximal y media en la palma para prevenir hiperextensión.
Tendones de la Mano
Los músculos extrínsecos se conectan a los huesos de los dedos mediante tendones largos que se extienden desde el antebrazo a través de la muñeca. Los tendones flexores en la palma ayudan a doblar los dedos, mientras los extensores en la parte superior ayudan a estirar los dedos.
Nervios de la Mano
Los tres nervios principales de la mano y muñeca se originan en el hombro y viajan por el brazo hasta la mano:
- Nervio cubital: cruza la muñeca por el canal de Guyon, proporcionando sensibilidad al meñique y mitad del anular
- Nervio mediano: cruza la muñeca por el túnel carpiano, proporcionando sensibilidad a la palma, pulgar, índice, medio y parte del anular
- Nervio radial: recorre el lado del pulgar del antebrazo y proporciona sensibilidad al dorso de la mano desde el pulgar hasta el dedo medio
Vasos Sanguíneos de la Mano
Las principales arterias son la cubital y radial, que suministran sangre a la palma, dedos y pulgar. La arteria cubital viaja junto al nervio cubital por el canal de Guyon en la muñeca. La radial es la arteria más grande de la mano, cruzando el frente de la muñeca cerca del pulgar. Otros vasos sanguíneos atraviesan el dorso de la muñeca para suministrar sangre al dorso de la mano, dedos y pulgar.
Si sufre lesiones, problemas o dolor en la mano y muñeca, permítanos ayudarle a recuperar la función, comodidad y calidad de vida.
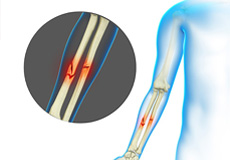
Adult Forearm Fractures
The forearm is made up of 2 bones, namely, the radius and ulna. The primary function of your forearm is rotation i.e., the ability to turn your palm up and down. The fracture of the forearm affects the ability to rotate your arm, as well as bend and straighten the wrist and elbow.
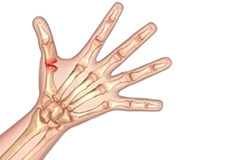
Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis and the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis. Arthritis affects various joints in the body and the arthritis in the hand affects the joint at the base of the thumb.
Arthritis of the Thumb
The forearm consists of two bones, the radius and ulna. The radius is the larger of the two forearm bones, and the region towards the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture or break in the distal end of the radius bone is known as a distal radius fracture.

Bennett's Fracture
Bennet's fracture is a break at the base of the first metacarpal bone (thumb bone) that meets the wrist at the first carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. The hand is composed of 3 types of bones: carpals or wrist bones, metacarpals or long hand bones, and phalanges or finger bones.

Boxer's Fracture
A boxer's fracture is a break in the neck of the fifth metacarpal bone of the hand (below the pinky finger) close to the knuckle. The hand is composed of 3 types of bones: carpal or wrist bones, metacarpals or long hand bones, and phalanges or finger bones.
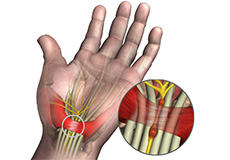
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.

De Quervain's Tendinosis
The muscles and bones of your hand are connected by thick flexible tissue called tendons. Tendons are covered by a thin soft sheath of tissue known as synovium. Extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus are two tendons located on the thumb side of the wrist.

Distal Radioulnar Joint (Druj) Arthritis
Distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) arthritis is an inflammatory condition characterized by gradual wearing away of the cartilaginous surface of the radioulnar joint resulting in significant pain, swelling, stiffness, and interference in the functioning of the wrist and/or arm.

Distal Radius Osteotomy to Correct Mal-Union (Crooked Painful Wrist)
The forearm consists of two bones, the radius, and the ulna. The radius is the larger of the two forearm bones, and the region closest to the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture or break in the distal end of the radius bone is known as a distal radius fracture.
Finger Dislocation
Finger dislocation is a condition in which the bone of your finger has moved away from its normal position.
Finger Sprain
Injuries that involve tearing or stretching of the ligaments of your fingers are termed as sprains. Sprains in the fingers are most often caused from a fall when you extend your arms to reduce the impact of the fall, or from overuse or repetitive activity of the thumb such as with texting.
Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts are swellings that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of wrists or hands. They can be found either at the top of the wrist, palm side of the wrist, end joint of a finger or at the base of a finger.
Mallet Finger
The finger joint is a hinge-joint that allows bending and straightening of the fingers. Each finger is composed of 3 phalanges joined by 2 interphalangeal joints (IP joints).

Malunion of a Fracture
Malunion of a fracture is a condition where the fractured ends of a bone heal in a misaligned position resulting in bone deformity. Malunions may occur in any bone fractures in the body often due to trauma.
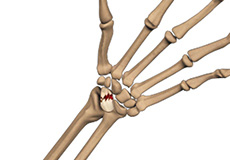
Scaphoid Fracture
The scaphoid bone is a small, boat-shaped bone in the wrist, which, along with 7 other bones, forms the wrist joint. It is present on the thumb side of the wrist and is at high risk for fractures. A scaphoid fracture is usually seen in young men aged 20 to 30 years. They can occur at two places: near the thumb or near the forearm.

Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) Wrist
Idiopathic avascular necrosis of the scaphoid (Preiser disease)
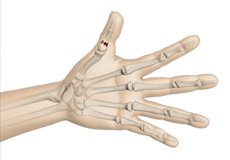
Thumb Fracture
A break or a crack in the bones of the thumb is known as a thumb fracture. Fractures may occur anywhere on the thumb, but a fracture at the base of the thumb, near the wrist, is considered the most serious.
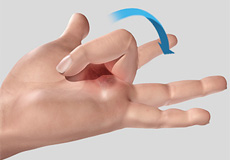
Trigger Finger
The ability to bend the fingers is governed by supportive tendons that connect muscles to the bones of the fingers. The tendons run along the length of the bone and are kept in place at intervals by tunnels of ligaments called pulleys.

Triscaphoid Joint Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of one or more joints in your body. Triscaphoid joint arthritis is the localized pain and inflammation of the shared joint between the 3 carpal bones of your wrist.

Ulnar Nerve Compression in Guyon's Canal
Ulnar nerve compression in Guyon's canal is a condition characterized by pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling sensation in the hand. The condition occurs when the ulnar nerve, the nerve that travels across the elbow from the shoulder to the hand, is compressed as it goes from the wrist into the hand through a space known as Guyon's canal.
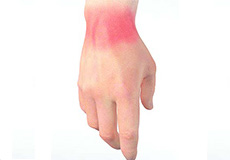
Wrist Injuries
The wrist is a commonly injured joint in the body. Problems include sprains and strains as well as fractures that can occur with lifting and carrying heavy objects, while operating machinery, bracing against a fall, or from sports-related injuries.

Wrist Pain
Wrist pain is defined as any ache or discomfort in the wrist. The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm.

Fracturas del Antebrazo en Adultos
El antebrazo está compuesto por dos huesos, llamados radio y cúbito. La función principal del antebrazo es la rotación, es decir, la capacidad de girar la palma hacia arriba y hacia abajo. La fractura del antebrazo afecta la capacidad de rotar el brazo, así como de flexionar y extender la muñeca y el codo. La rotura del radio o el cúbito en la parte media del hueso requiere una gran fuerza y se observa con mayor frecuencia en adultos.

Artritis de la Mano y la Muñeca
La artritis es una condición inflamatoria de las articulaciones. Existen varios tipos de artritis, y el tipo más común es la osteoartritis o artritis por desgaste. La artritis afecta diversas articulaciones del cuerpo, y la artritis en la mano suele afectar la articulación en la base del pulgar. La artritis también puede afectar las articulaciones de otros dedos.

Arthritis of the Thumb
The forearm consists of two bones, the radius and ulna. The radius is the larger of the two forearm bones, and the region towards the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture or break in the distal end of the radius bone is known as a distal radius fracture.

Fractura de Bennett
La fractura de Bennett es una rotura en la base del primer hueso metacarpiano (hueso del pulgar) que se une con la muñeca en la primera articulación carpometacarpiana (CMC). La mano está compuesta por tres tipos de huesos:

Fractura de Boxeador
Una fractura de boxeador es una rotura en el cuello del quinto hueso metacarpiano de la mano (debajo del dedo meñique), cerca del nudillo. La mano está compuesta por 3 tipos de huesos: los huesos carpianos o huesos de la muñeca, los metacarpos o huesos largos de la mano, y las falanges o huesos de los dedos. Los metacarpos consisten en cinco huesos largos que conectan el carpo con las falanges.

Síndrome del Túnel Carpiano
El síndrome del túnel carpiano es una afección común, dolorosa y progresiva causada por la compresión del nervio mediano en la zona de la muñeca.

Tendinosis de De Quervain
Los músculos y huesos de la mano están conectados por un tejido grueso y flexible llamado tendón. Los tendones están cubiertos por una fina y suave vaina de tejido llamada sinovio. El extensor corto del pulgar (extensor pollicis brevis) y el abductor largo del pulgar (abductor pollicis longus) son dos tendones ubicados en el lado del pulgar de la muñeca.

Artritis de la Articulación Radiocubital Distal (DRUJ)
La artritis de la articulación radiocubital distal (DRUJ) es una condición inflamatoria caracterizada por el desgaste gradual de la superficie cartilaginosa de la articulación radiocubital, lo que provoca dolor significativo, hinchazón, rigidez e interferencia en la función de la muñeca y/o el brazo.

Osteotomía de Radio Distal para Corregir una Mala Unión (Muñeca Dolorosa y Deformada)
El antebrazo consta de dos huesos: el radio y el cúbito. El radio es el más grande de los dos, y la región más cercana a la muñeca se llama extremo distal. Una fractura o rotura en esta zona se conoce como fractura de radio distal.

Luxación de Dedo
La luxación de dedo es una condición en la que el hueso del dedo se desplaza de su posición normal.

Esguince de Dedo
Las lesiones que implican el desgarro o estiramiento de los ligamentos de los dedos se denominan esguinces. Los esguinces en los dedos suelen producirse por una caída en la que se extienden los brazos para reducir el impacto, o por el uso excesivo o actividad repetitiva del pulgar, como al enviar mensajes de texto.

Quiste Sinovial
Los quistes sinoviales son hinchazones que se desarrollan con mayor frecuencia a lo largo de los tendones o articulaciones de las muñecas o las manos. Pueden encontrarse en la parte superior de la muñeca, el lado de la palma, la articulación final de un dedo o en la base de un dedo.

Dedo en Martillo
La articulación del dedo es una articulación en bisagra que permite la flexión y extensión de los dedos. Cada dedo está compuesto por 3 falanges unidas por 2 articulaciones interfalángicas (articulaciones IP).

Consolidación Viciosa de una Fractura (Malunion of a Fracture)
Malunion of a fracture is a condition where the fractured ends of a bone heal in a misaligned position resulting in bone deformity. Malunions may occur in any bone fractures in the body often due to trauma.

Fractura del Hueso Escafoides (Scaphoid Fracture)
El hueso escafoides es un hueso pequeño con forma de barco ubicado en la muñeca, que junto con otros siete huesos forma la articulación de la muñeca. Se encuentra en el lado del pulgar y tiene un alto riesgo de fractura. Las fracturas de escafoides suelen observarse en hombres jóvenes de entre 20 y 30 años. Estas fracturas pueden ocurrir en dos zonas: cerca del pulgar o cerca del antebrazo.

Consolidación Viciosa de una Fractura
El colapso avanzado escafolunato (SLAC, por sus siglas en inglés) de la muñeca es una condición degenerativa que afecta la articulación de la muñeca debido a una inestabilidad crónica entre el hueso escafoides y el hueso semilunar.

Fractura del Pulgar
Una fractura del pulgar es una rotura o grieta en los huesos del pulgar. Las fracturas pueden ocurrir en cualquier parte del pulgar, pero una fractura en la base del pulgar, cerca de la muñeca, se considera la más grave.

Dedo en Gatillo
La inflamación del tenosinovio conduce a una condición llamada dedo en gatillo, también conocida como tenosinovitis estenosante o tendinitis flexora. En esta condición, uno de los dedos o el pulgar de la mano queda atrapado en una posición doblada.

Artritis de la Articulación Triescafoidea
La artritis es una condición inflamatoria de una o más articulaciones de tu cuerpo. La artritis de la articulación triescafoidea es el dolor e inflamación localizada de la articulación compartida entre los 3 huesos carpianos de tu muñeca. Estos huesos se llaman escafoides, trapecio y trapezoide y están presentes en la base del pulgar.

Compresión del Nervio Cubital en el Canal de Guyon
La compresión del nervio cubital en el canal de Guyon es una condición caracterizada por dolor, entumecimiento, debilidad y sensación de hormigueo en la mano. La condición ocurre cuando el nervio cubital, el nervio que viaja desde el hombro hasta la mano pasando por el codo, se comprime al pasar de la muñeca hacia la mano a través de un espacio conocido como canal de Guyon.

Lesiones de Muñeca
La muñeca es una articulación comúnmente lesionada en el cuerpo. Los problemas incluyen esguinces y distensiones, así como fracturas que pueden ocurrir al levantar y cargar objetos pesados, al operar maquinaria, al intentar amortiguar una caída o por lesiones relacionadas con el deporte.

Dolor de Muñeca
El dolor de muñeca se define como cualquier molestia o incomodidad en la muñeca. La muñeca está compuesta por dos huesos en el antebrazo, el radio y el cúbito, y ocho pequeños huesos carpianos en la palma. Los huesos se unen para formar múltiples articulaciones grandes y pequeñas. Un trauma o lesión en uno o más de estos huesos resulta en dolor de muñeca.
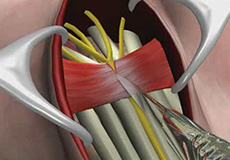
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by the compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.

Finger Joint Fusion
The hands are made up of 27 bones, which are grouped into carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. Each bone is separated by the articular cartilage, which helps provide smooth gliding movements of the fingers.
Hand Fracture Surgery
The hand is one of the most flexible and useful parts of our body. Because of overuse in various activities, the hands are more prone to injuries, such as sprains and strains, fractures and dislocations, lacerations and amputations while operating machinery, bracing against a fall and sports-related injuries.

Lrti For Thumb Cmc Arthritis
The joint located at the base of the thumb is known as the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. The thumb CMC joint is where the metacarpal bone of the thumb connects to the trapezium (carpal) bone of the wrist. The CMC is the joint most affected in thumb arthritis.

Nerve Decompression Of The Upper Extremities
Nerve decompression of the upper extremities, also called peripheral nerve decompression, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure employed to relieve pressure on an entrapped or pinched nerve (neuroma) for the treatment of conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome, the two most common nerve compression syndromes.
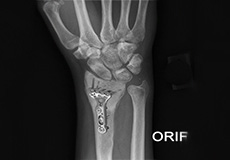
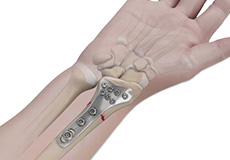
ORIF of Distal Radius Fracture
The forearm consists of two bones, the radius and ulna. The radius is the larger of the two forearm bones, and the region towards the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture or break in the distal end of the radius bone is known as a distal radius fracture.

ORIF of the Forearm Fractures
The forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. A break in both or either of the bones is known as forearm fracture. Forearm fractures can occur near the wrist, near the elbow, or in the middle of the forearm. A forearm fracture affects the ability to rotate your arm, as well as bend and straighten the wrist and elbow.
Surgery For Thumb And Digit Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis; the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis that affects the joint at the base of the thumb. Thumb arthritis is more common in women than men, and usually occurs after the age of 40 years.
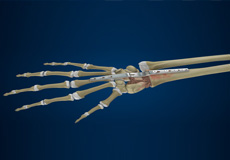
Total Wrist Arthrodesis
The wrist joint is one of the most complex joints in the human body. Numerous joints and bones contribute to the strength and stability of the wrist. The wrist is made up of eight separate small bones called carpal bones.
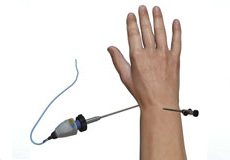
Wrist Arthroscopy
Your wrist is a complex joint made up of eight small bones called carpal bones. These bones are supported by connecting ligaments. Various conditions can affect your wrist joint such as carpal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis and others.

Wrist Fracture Fixation
Wrist fractures are breaks in any of the bones that form your wrist joint.

Wrist Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
Open reduction and internal fixation of the wrist is a surgical technique employed for the treatment of severe wrist fractures to restore normal anatomy and improve range of motion and function.

Liberación del Túnel Carpiano
Para ayudarte a conversar sobre la cirugía de liberación del túnel carpiano como una opción de tratamiento con tu cirujano ortopédico, aquí tienes un desglose de este procedimiento quirúrgico.

Fusión de la Articulación del Dedo
La artritis se desarrolla cuando el cartílago se desgasta, provocando dolor, rigidez e inflamación en las articulaciones. Aunque puede afectar cualquier articulación del cuerpo, las más comúnmente afectadas son las pequeñas articulaciones de los dedos.

Cirugía de Fractura de Mano
La mano es una de las partes más “ocupadas” de nuestro cuerpo, lo que la hace más propensa a lesiones, tales como esguinces y distensiones, fracturas y dislocaciones, entre otras. Una fractura de mano ocurre cuando uno de los huesos de la mano se rompe.

Cirugía LRTI para la Artritis CMC del Pulgar
La articulación ubicada en la base del pulgar se conoce como articulación carpometacarpiana (CMC). La CMC es la articulación más afectada en la artritis del pulgar.

Descompresión Nerviosa de las Extremidades Superiores
La descompresión nerviosa de las extremidades superiores, también llamada descompresión de nervio periférico, es un procedimiento quirúrgico mínimamente invasivo que se utiliza para aliviar la presión sobre un nervio atrapado o pinzado (neuroma) para el tratamiento de afecciones como el síndrome del túnel carpiano y el síndrome del túnel cubital, los dos síndromes de compresión nerviosa más comunes.

Cirugía ORIF para Fracturas de Radio Distal
Para ayudarte a discutir la cirugía ORIF como opción de tratamiento para una fractura del radio distal con tu cirujano ortopédico, aquí tienes un desglose de este procedimiento quirúrgico.

ORIF de Fracturas del Antebrazo
Para ayudarte a discutir la ORIF como una opción de tratamiento para una fractura de antebrazo con tu cirujano ortopédico, aquí tienes un desglose de este procedimiento quirúrgico.

Cirugía para la Artritis del Pulgar y los Dedos
La artritis es una condición inflamatoria de las articulaciones. Existen varios tipos de artritis; el tipo más común es la osteoartritis o artritis por desgaste, que afecta la articulación en la base del pulgar. La artritis del pulgar es más común en las mujeres que en los hombres y generalmente ocurre después de los 40 años de edad.

Artrodesis Total de Muñeca
La articulación de la muñeca es una de las más complejas del cuerpo humano. Numerosas articulaciones y huesos contribuyen a la fuerza y estabilidad de la muñeca. La muñeca está compuesta por ocho huesos pequeños separados llamados huesos carpianos. Los huesos carpianos conectan los dos huesos del antebrazo, el radio y el cúbito, con los huesos de la mano.

Artroscopia de Muñeca
Para ayudarte a hablar con tu cirujano ortopédico sobre la cirugía de artroscopia de muñeca como opción de tratamiento para tu muñeca, aquí tienes un desglose de este procedimiento quirúrgico.

Fijación de fractura de muñeca
Las fracturas de muñeca son roturas en cualquiera de los huesos que forman tu articulación de la muñeca.

Reducción Abierta y Fijación Interna de la Muñeca
La reducción abierta y fijación interna de la muñeca es una técnica quirúrgica empleada para el tratamiento de fracturas graves de muñeca con el fin de restaurar la anatomía normal y mejorar el rango de movimiento y la función.
