Comprehensive Guide to Knee Anatomy and Conditions
The knee undergoes a lot of stress every single day, especially for people who are physically active. As the years go by, that stress can add up to wear and tear that decreases mobility and comfort, and interferes with daily activities. The knee can also suffer from injuries or disease, resulting in knee problems and conditions that can be excruciatingly painful and extremely debilitating. If you have knee problems, you need to talk to us.
To help you discuss knee problems, conditions and treatment options with your surgeon, here's a breakdown of the anatomy of the knee.
Guía integral de la anatomía y condiciones de la rodilla
La rodilla soporta mucho estrés todos los días, especialmente en personas que son físicamente activas. Con el paso de los años, ese estrés puede acumularse y provocar desgaste que disminuye la movilidad y la comodidad, interfiriendo con las actividades diarias. La rodilla también puede sufrir lesiones o enfermedades, lo que resulta en problemas y condiciones de rodilla que pueden ser extremadamente dolorosos y sumamente incapacitantes. Si tiene problemas de rodilla, necesita hablar con nosotros.
Para ayudarle a conversar sobre los problemas, condiciones y opciones de tratamiento de la rodilla con su cirujano, aquí tiene un desglose de la anatomía de la rodilla.
- AnatomyAnatomía
- Conditions Condiciones
- Procedures Cirugías
Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee's normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Bones and Cartilage of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones:
- The thigh bone, or femur
- The shinbone, or tibia
To reduce friction between bones, all surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage, which provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid that lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones.
Between the femur and tibia are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci, which provide stability and help in load-bearing by preventing weight from concentrating onto a small area. The menisci also absorb shock and act as a cushion during walking, running, and jumping.
Ligaments of the Knee
The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint, and include two groups:
- Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee, and prevent the knee from moving too far during side to side motion.
- Cruciate ligaments are present inside the knee joint, and control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee which enable movement of the knee joint:
- The quadriceps muscles straighten the knee when they contract.
- The hamstrings bend the knee when they contract.
Tendons of the Knee
The quadriceps tendon attaches the patella to the quadriceps. The patella tendon attaches the patella to the tibia. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon work together to straighten the knee, while the hamstring tendon attaches the hamstring muscles to the back of the leg. You don't have to walk through life in pain. If you have knee problems or conditions, let us help you get back on your feet - and get back your life.
Anatomía de la Rodilla
La rodilla es una articulación compleja compuesta por diferentes estructuras: huesos, tendones, ligamentos y músculos. Todos ellos trabajan juntos para mantener la función normal de la rodilla y proporcionar estabilidad durante el movimiento.
Huesos y cartílago de la rodilla
La rodilla es una articulación en bisagra formada por dos huesos:
- El hueso del muslo, o fémur
- El hueso de la espinilla, o tibia
Para reducir la fricción entre los huesos, todas las superficies implicadas en el movimiento están recubiertas por una capa blanca, brillante y resbaladiza llamada cartílago articular, que proporciona una superficie suave que facilita el movimiento.
Para reducir aún más la fricción, la articulación de la rodilla está recubierta por una membrana sinovial que produce un líquido claro y espeso que lubrica y nutre el cartílago y los huesos.
Entre el fémur y la tibia se encuentran dos estructuras cartilaginosas en forma de C llamadas meniscos, que proporcionan estabilidad y ayudan en la carga de peso al evitar que este se concentre en un área pequeña. Los meniscos también absorben el impacto y actúan como amortiguadores durante la caminata, la carrera y los saltos.
Ligamentos de la rodilla
Los ligamentos de la rodilla estabilizan la articulación e incluyen dos grupos:
- Los ligamentos colaterales están presentes a ambos lados de la rodilla y evitan que la rodilla se mueva demasiado durante los movimientos de lado a lado.
- Los ligamentos cruzados están presentes dentro de la articulación y controlan el movimiento hacia adelante y hacia atrás de la rodilla. El ligamento cruzado en la parte delantera de la rodilla se llama ligamento cruzado anterior (LCA) y el de la parte posterior se llama ligamento cruzado posterior (LCP).
Músculos de la rodilla
Existen dos músculos principales en la rodilla que permiten su movimiento:
- Los músculos cuádriceps enderezan la rodilla cuando se contraen.
- Los isquiotibiales doblan la rodilla cuando se contraen.
Tendones de la rodilla
El tendón del cuádriceps conecta la rótula con el cuádriceps. El tendón rotuliano conecta la rótula con la tibia. El músculo cuádriceps, el tendón del cuádriceps y el tendón rotuliano trabajan juntos para enderezar la rodilla, mientras que el tendón de los isquiotibiales conecta los músculos isquiotibiales con la parte posterior de la pierna.
No tiene por qué vivir con dolor. Si tiene problemas o condiciones en la rodilla, permítanos ayudarle a ponerse de pie nuevamente… y a recuperar su vida.
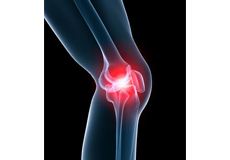
Knee Pain
Knee pain is a common condition affecting individuals of various age groups. It not only affects movement but also impacts your quality of life. An injury or disease of the knee joint or any structure surrounding the knee can result in knee pain. A precise diagnosis of the underlying cause is important to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
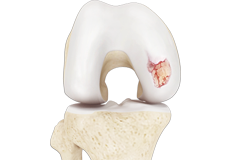
Knee Arthritis
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. Arthritis is a general term covering numerous conditions where the joint surface or cartilage wears out.
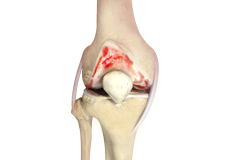
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease in which the lining of your joints becomes inflamed, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It is an autoimmune disease because it occurs when your immune system, which normally fights against infection, starts destroying healthy joints.

Dolor de Rodilla
El dolor de rodilla es una condición común que afecta a personas de diferentes grupos de edad. No solo limita el movimiento, sino que también impacta en la calidad de vida. Una lesión o enfermedad de la articulación de la rodilla, o de cualquiera de las estructuras que la rodean, puede provocar dolor de rodilla.

Artritis de cadera
La superficie articular está recubierta por una capa lisa que permite un movimiento sin dolor en la articulación. La artritis es un término general que abarca numerosas condiciones en las que la superficie articular o el cartílago se desgastan. Esta superficie puede deteriorarse por varias razones; en muchos casos, la causa exacta no se conoce.

Artritis Reumatoide
La artritis reumatoide es una enfermedad inflamatoria crónica en la que el revestimiento de las articulaciones se inflama, causando dolor, hinchazón y rigidez. Es una enfermedad autoinmune porque ocurre cuando su sistema inmunológico, que normalmente combate las infecciones, comienza a destruir las articulaciones sanas.
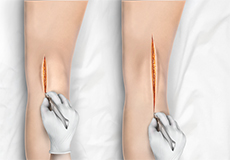
Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is a very successful surgical treatment for knee arthritis. Over the years, minimally invasive knee replacement surgical techniques have been developed to lessen tissue trauma and improve patient outcomes.

Partial Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement.
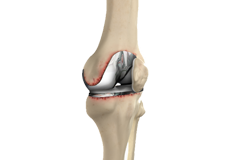
Knee Revision
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and may require a second revision surgery.

Reemplazo de Rodilla Mínimamente Invasivo
La cirugía de reemplazo total de rodilla es un tratamiento quirúrgico mínimamente invasivo y conservador de músculos para la artritis de rodilla, que reduce el trauma a los tejidos y mejora los resultados para el paciente.

Reemplazo Parcial de Rodilla
La artritis es la inflamación de una articulación que causa dolor, hinchazón e rigidez. La osteoartritis es la forma más común de artritis de rodilla, en la que el cartílago articular se desgasta gradualmente.

Revisión de rodilla
La artritis de las articulaciones de la rodilla es causada por el desgaste del cartílago articular blando que amortigua las articulaciones y ayuda en el movimiento suave de los huesos de la articulación, lo que puede causar dolor intenso, incomodidad e inmovilidad.
